Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 061 |
| Age: | 51 |
| Clinical presentation: | Perimenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a lump in the right breast that she noticed 4 months ago. On examination, she was found to have a lump in the right breast with irregular margins. No history of trauma, fever, pain, or nipple discharge. |
Mammography:
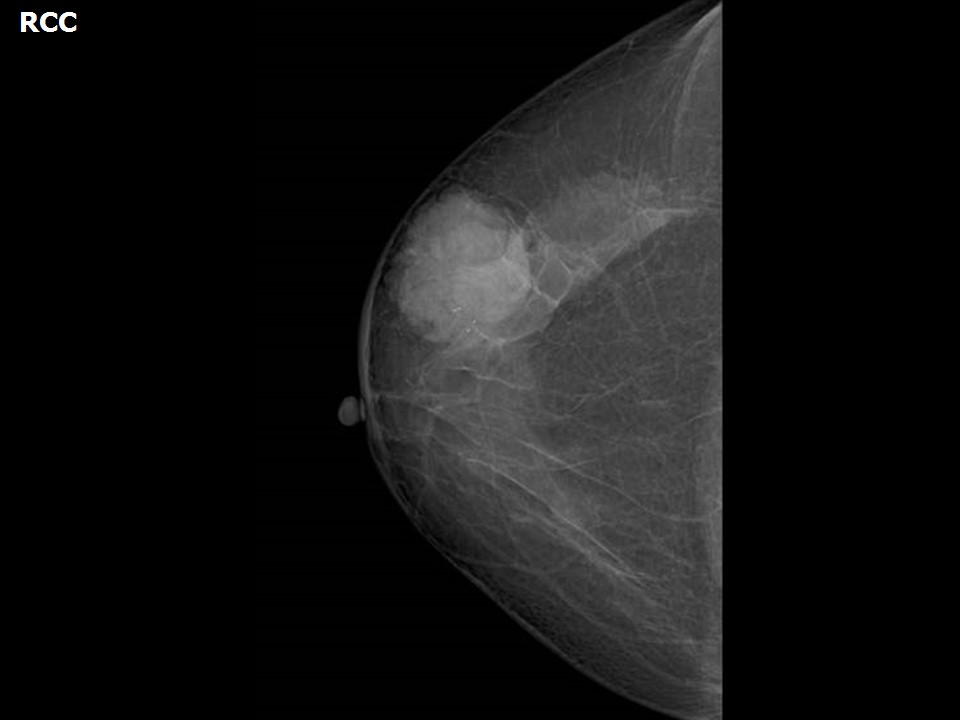
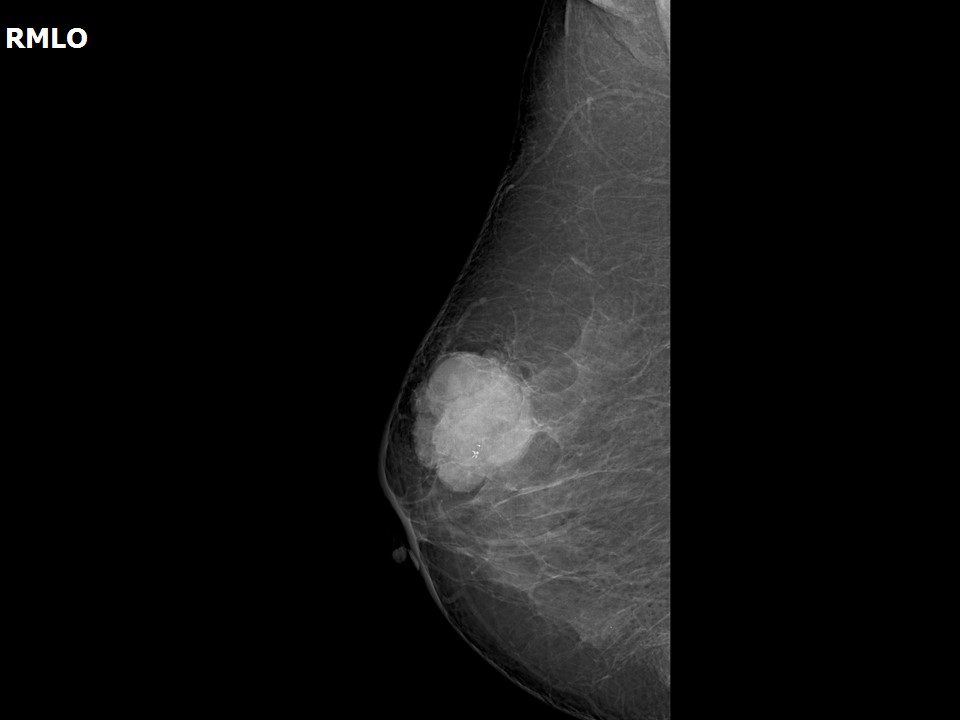
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10–11 o’clock, anterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 4.6 × 4.2 × 4.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Microlobulated |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Coarse heterogeneous |
| • Distribution: | Within mass |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
Ultrasound:
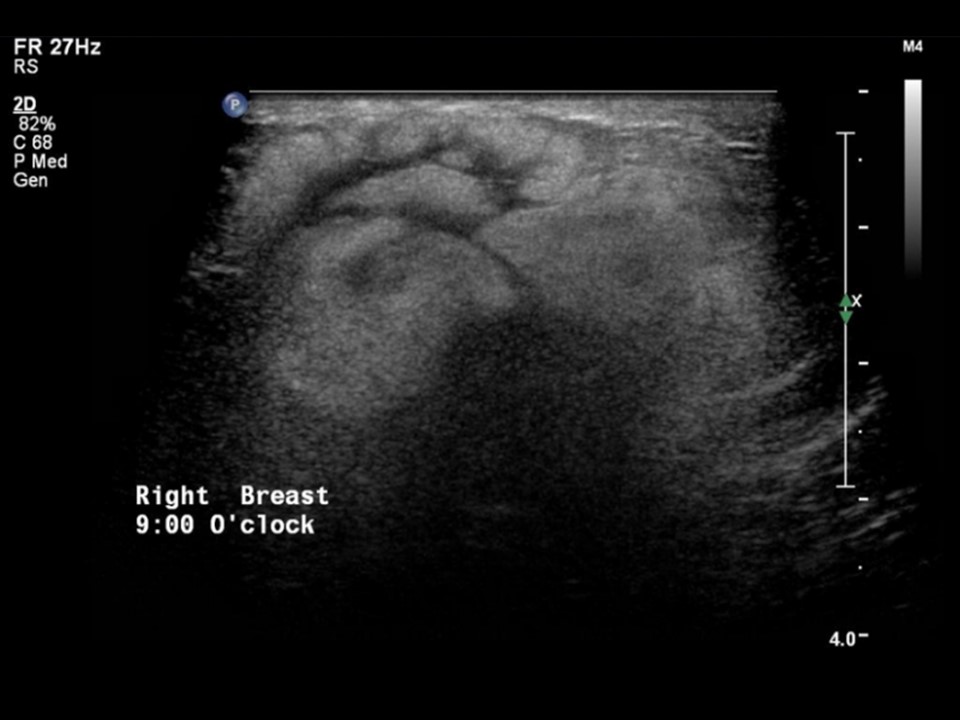
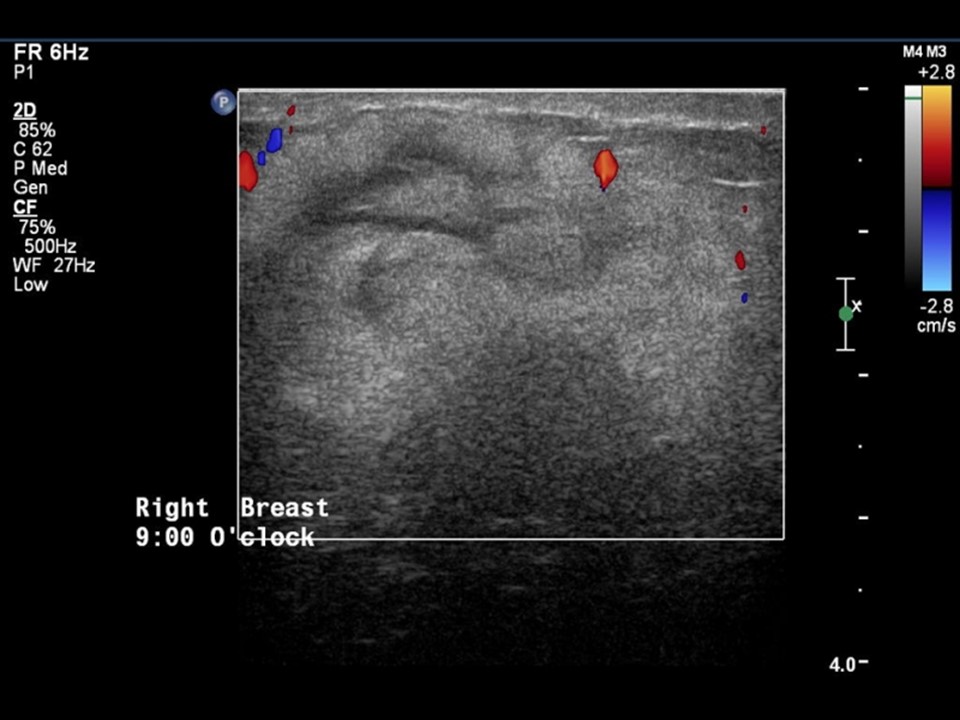
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, outer quadrants | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, outer quadrants |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 5.0 × 2.6 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for core biopsyCytology:
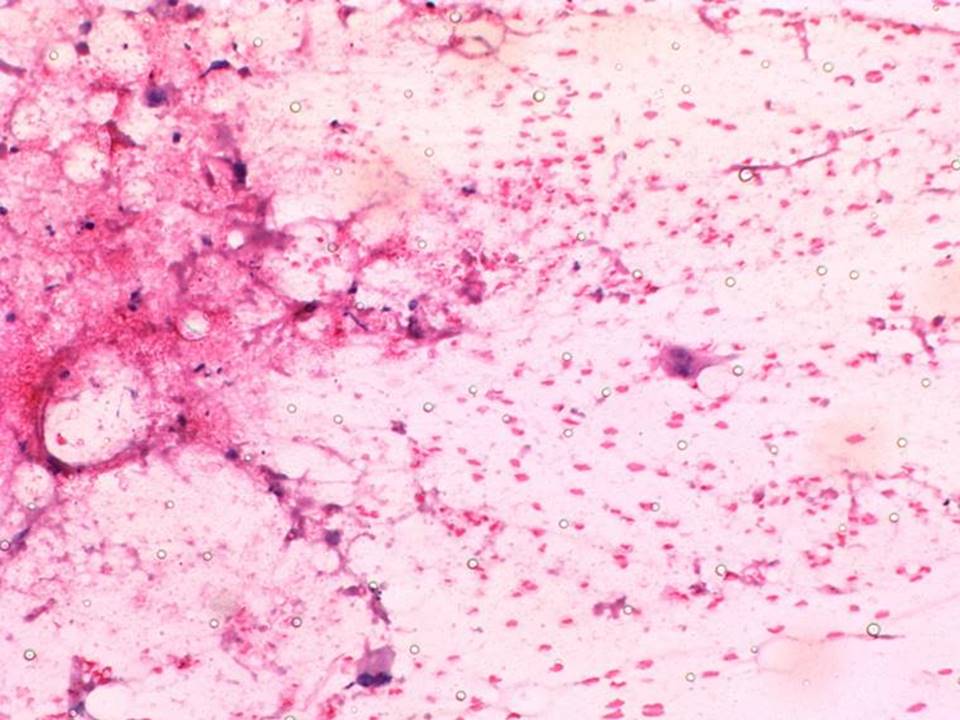
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Mainly necrotic debris with a few scattered single isolated malignant epithelial cells |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Malignancy |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
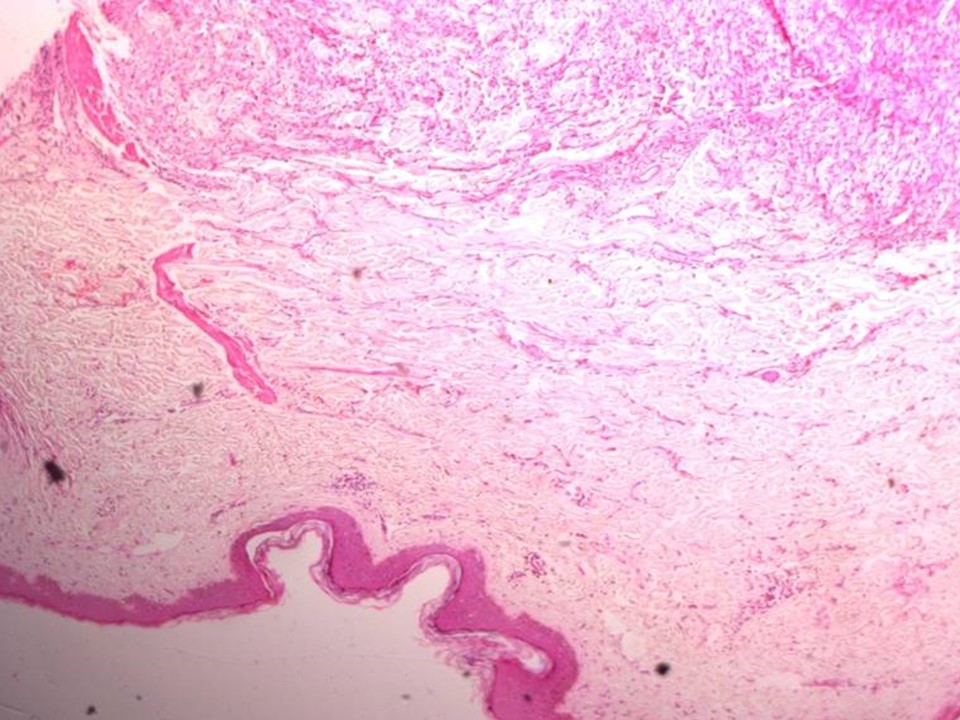
Histopathology:
MRM
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | MRM |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
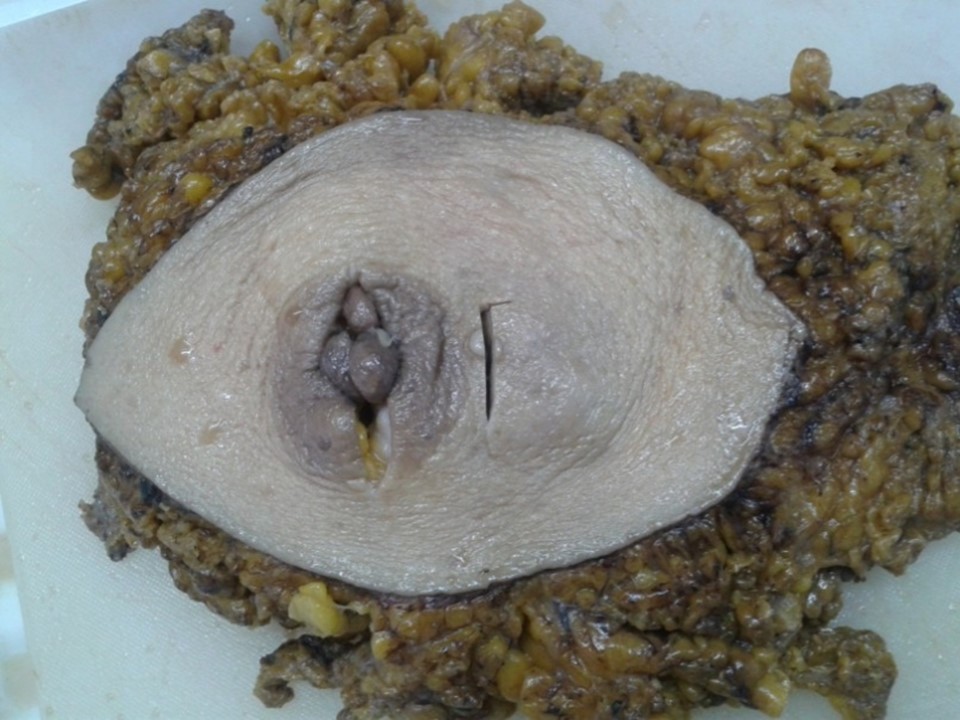
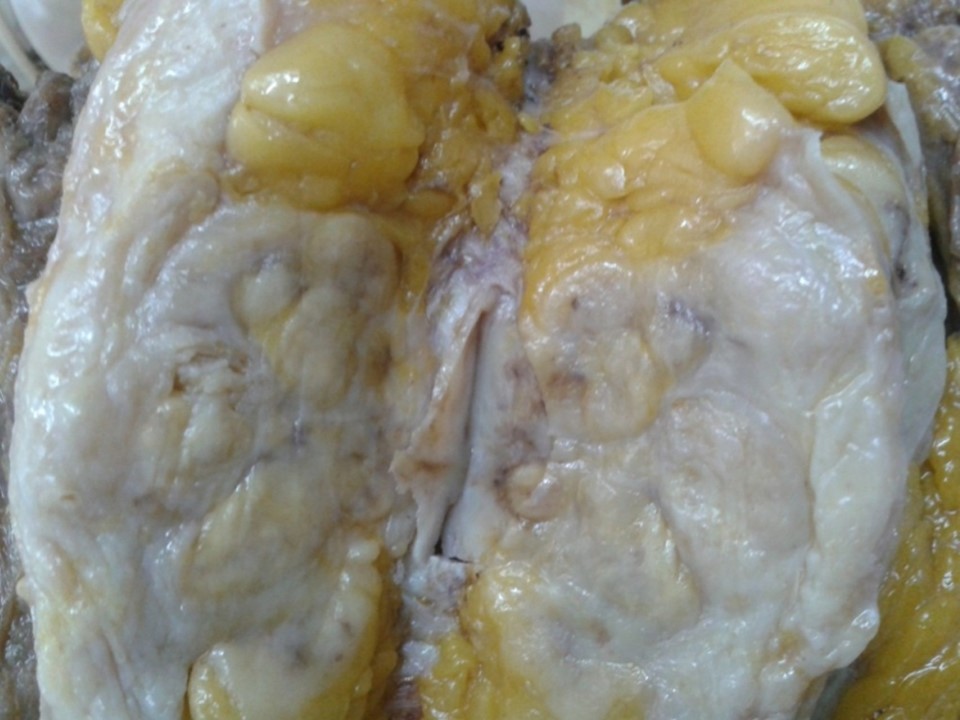
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Right radical mastectomy specimen (24.0 × 17.0 × 4.0 cm) with an elliptical piece of skin including nipple and areola (16.0 × 10.0 cm). A small pedunculated polyp (1.0 × 1.0 × 0.5 cm) is attached to the nipple. A nodule lateral to areolar region (0.7 × 0.5 × 0.5 cm) is attached to the skin. On sectioning, a fleshy, greyish white, well-circumscribed tumour (5.0 × 4.0 × 5.5 cm) is seen. The cut surface of the tumour is solid, bulging, firm, and greyish white with pushing margins. The tumour is seen to extend to the skin. Distance from base is 1.0 cm. |
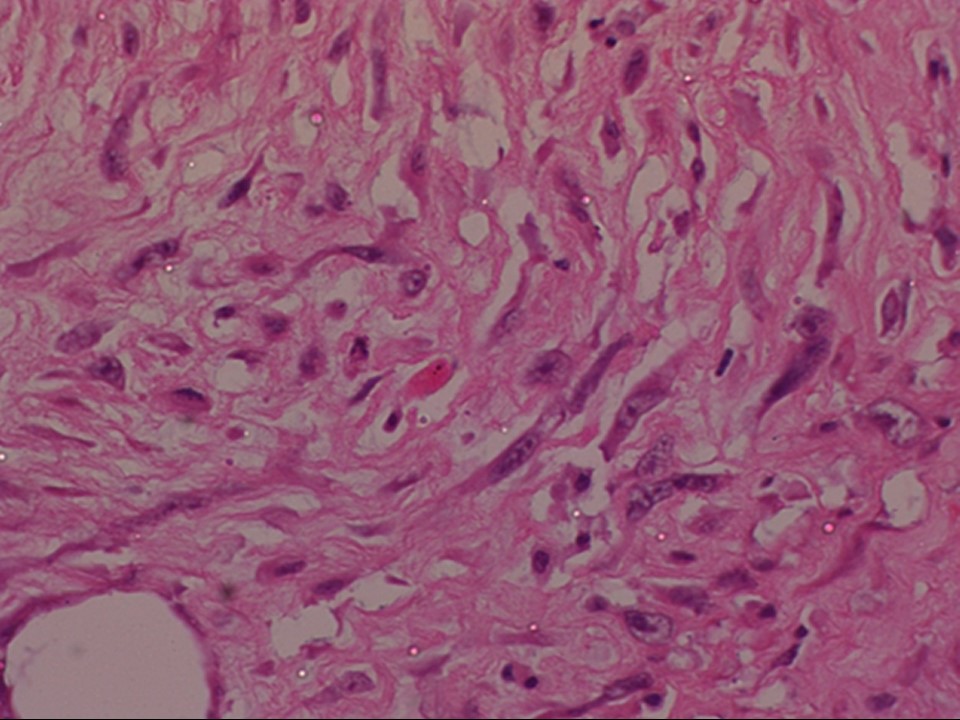
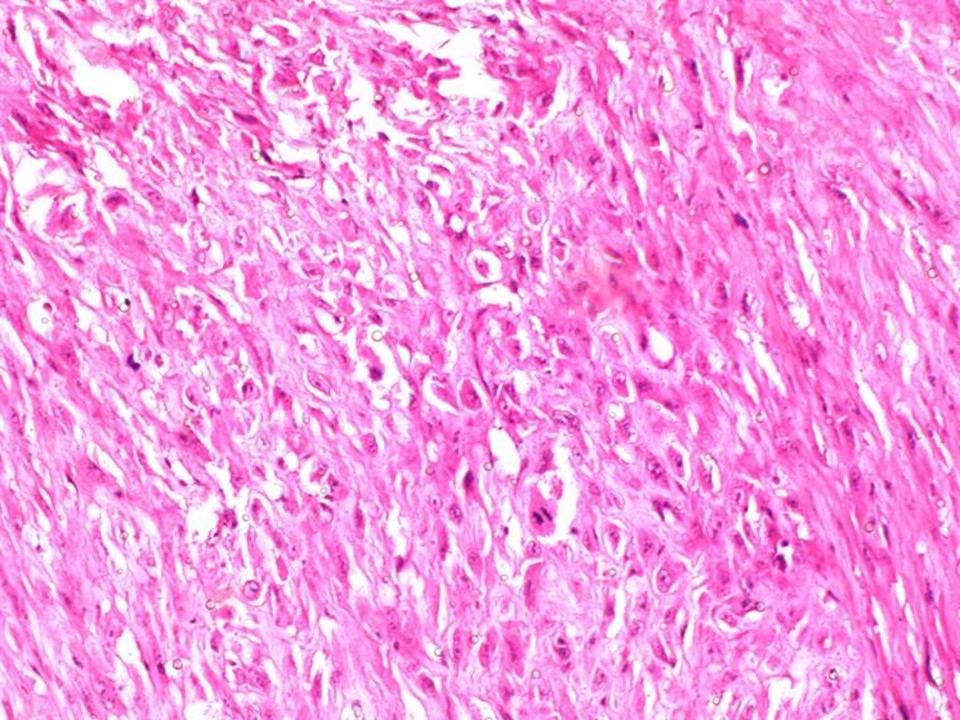
| ‣ Histological type: | Spindle cell stromal sarcoma arising in phyllodes tumour |
| ‣ Histological grade: | High grade |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 30 per 10 hpf |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 5.5 cm in greatest dimension |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 0/5 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | nil |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | nil |
| ‣ Margins: | Nodule on skin shows tumour; posterior margin is free of tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT4bN0 (ipsilateral satellite skin nodule) |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | On IHC, the tumour cells express vimentin positivity whereas ER, PR, HER2/neu, E cadherin, and CK are negative. M1B1 labelling index is 20% |
| ‣ Comments: | A large area of necrosis was seen in the tumour. The pedunculated polyp at the nipple showed a fibroepithelial polyp. There was no malignancy |
Case summary:
| Perimenopausal woman presented with right breast lump. Diagnosed as neoplastic mass lesion in right breast, BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as malignancy present on cytology, and as spindle cell stromal sarcoma arising in phyllodes tumour, pT4bN0 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|